Jutta Horstmann www.osdbmigration.org Migration to Open Source Databases
Slide 1

Slide 2
whoami ● Unix/Linux sysadmin ● DBA, developer (Informix) ● DB developer (Oracle) ● Web stuff (MySQL, PostgreSQL) ● Claim to Fame: OpenUsability.org ● Comp Sci Diploma Thesis: Migration to Open Source Databases Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 3

Agenda ● What’s this? ➔ About ● Why migrate? ➔ Pros and Cons ● Where to migrate? ➔ Open Source Databases ● How to migrate? ➔ Workflow: Activities ● What to migrate? ➔ Workflow: Assets Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 4

Migration? “The process of changing from the use of one platform, environment, IT system, etc., to another, esp. in such a way as to avoid interruptions in service.” (Oxford English Dictionary) Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 5

Migration: Objectives The target system: The migration workflow: ● same functionality ● Minimize risk ● extendable ● Stay on budget ● incorporate all data ● Deliver in due time ● modern hardware, ● Minimize downtime software, architecture Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 6
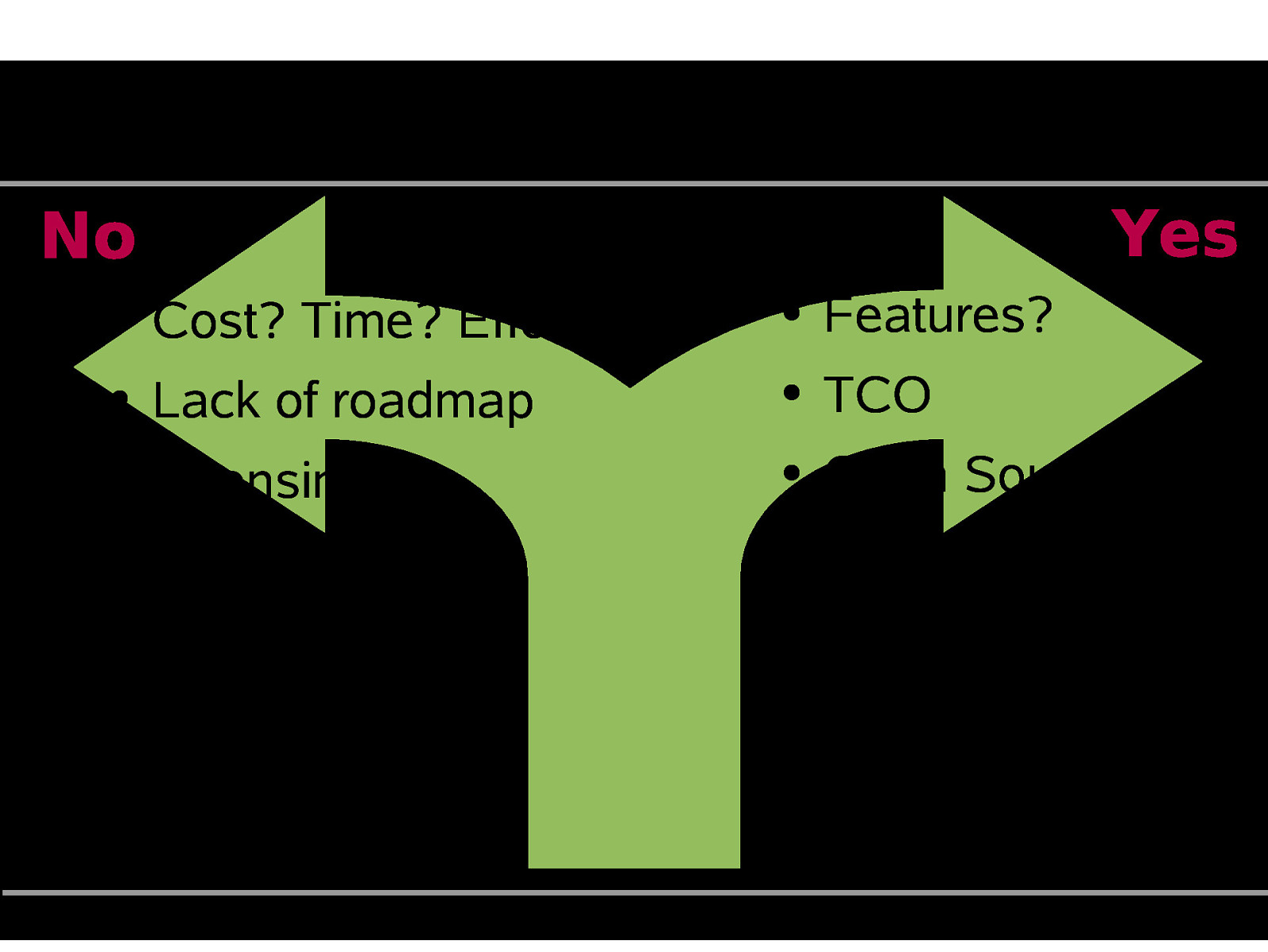
OSDB Migration:Pros and Cons Yes No ● Cost? Time? Effort? ● Features? ● Lack of roadmap ● TCO ● Licensing ● Open Source ● ISV Support – Code Maintenance – Community ● ● ● Accountability Features ● Standards ● Security ● Independence Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 7
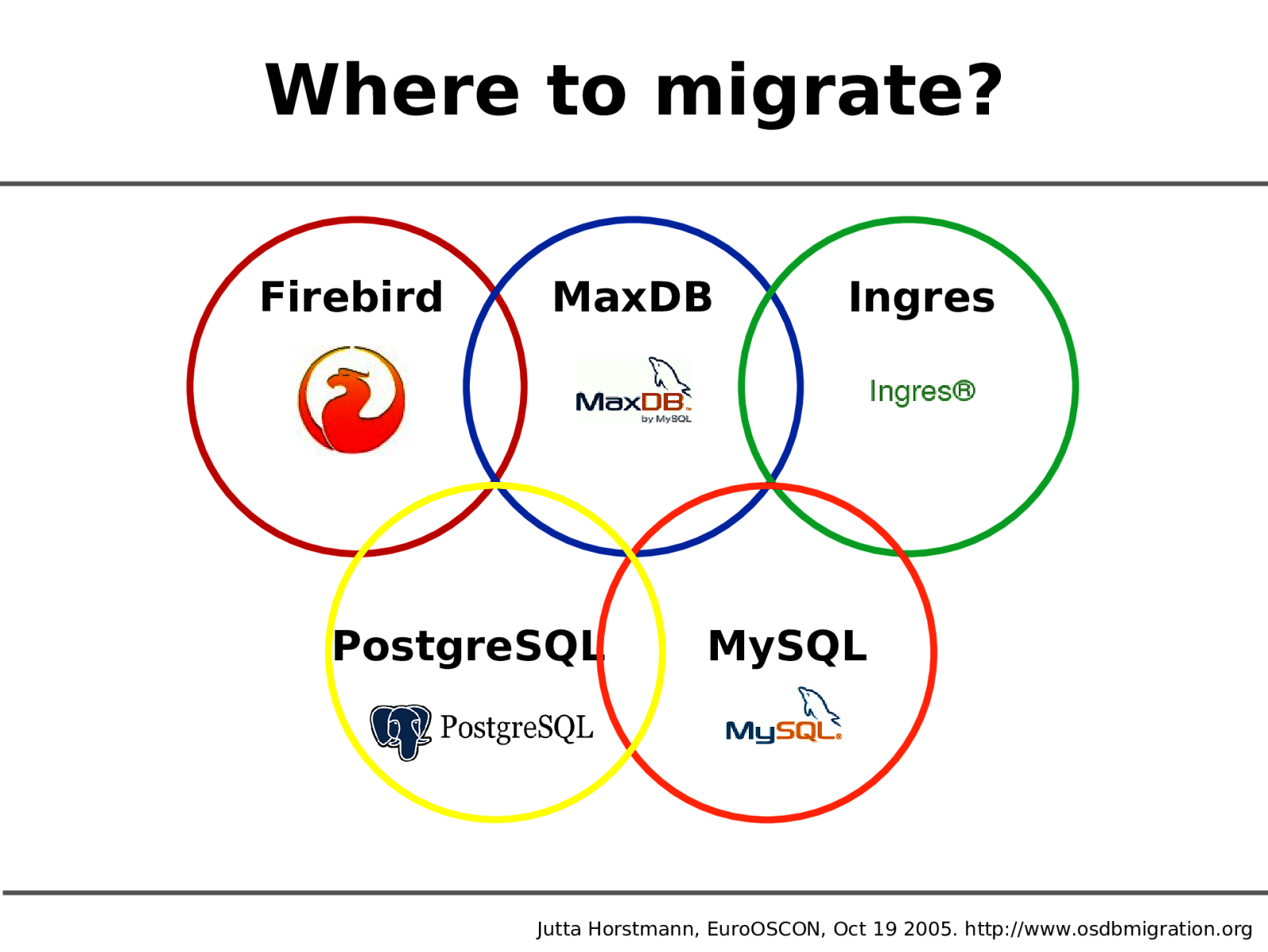
Where to migrate? Firebird MaxDB PostgreSQL Ingres MySQL Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 8
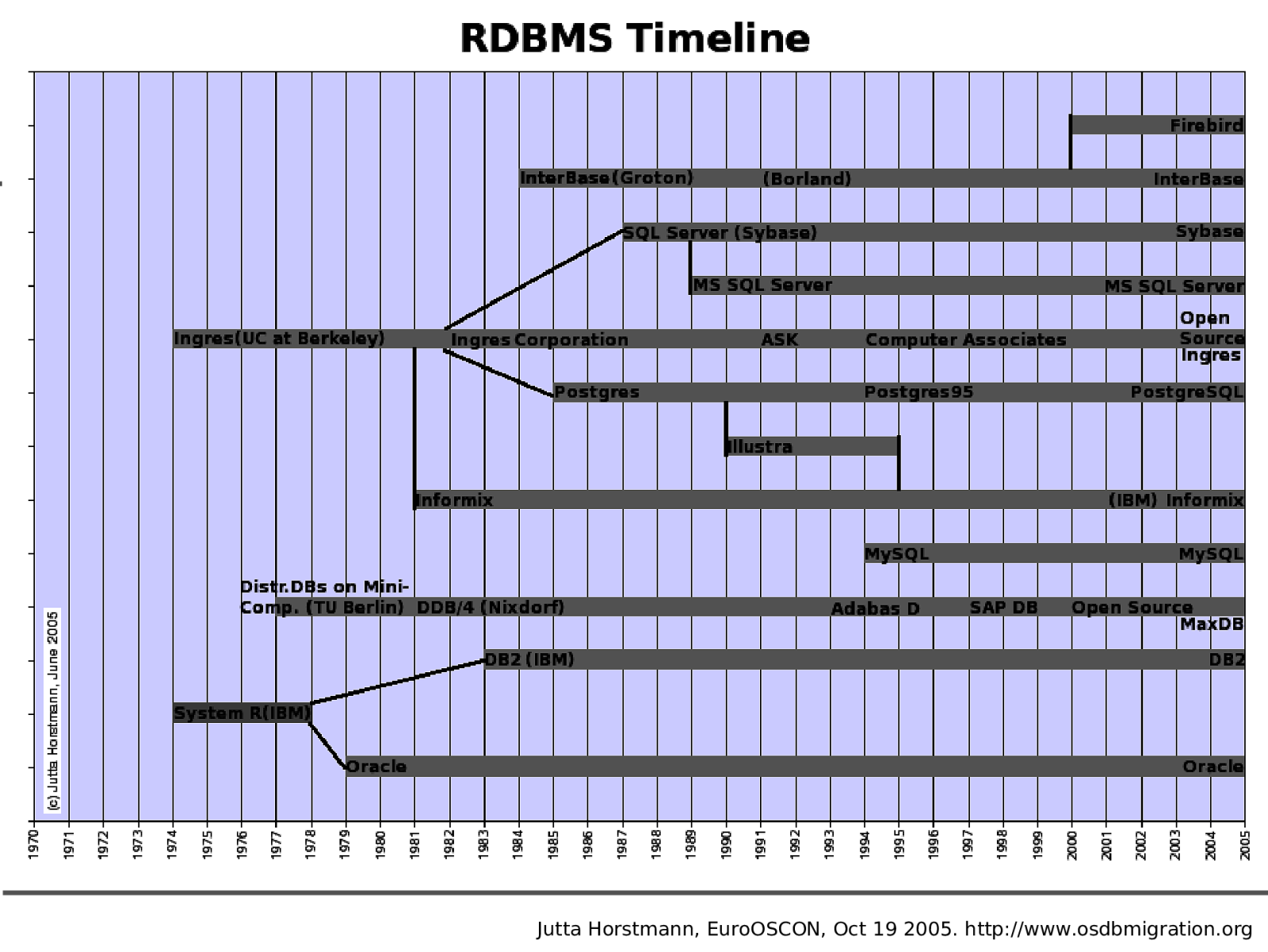
Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 9

Enterprise-Level? Requirements: ● Advanced data integrity mechanisms ● Advanced database objects ● Advanced SQL features ● Advanced features, tools, support for Performance and scalability – (High) Availability – Security – Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 10

OSDB Features Firebird 1.5 Ingres r3 MaxDB 7.5 MySQL 4.1 Advanced Indexing MyISAM GIS support MyISAM MVCC InnoDB Two phase commit UD Functions UD data types Updatable Views v.5.0 v.7.6 PostgreSQL 8.0 v.8.1 v.5.0 v.5.0 Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 11

Performance / Scalability Firebird 1.5 Ingres r3 MaxDB 7.5 MySQL 4.1 PostgreSQL 8.0 Tablespaces Table Partitioning v.8.1 Parallelization Built-In Clustering Built-In Load Balancing Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 12

How to migrate? Database Migration Workflow ● Activity-Centered? ● Asset-Centered? ● Proposal: Mixed-Model Workflow ● Walk-Through Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 13
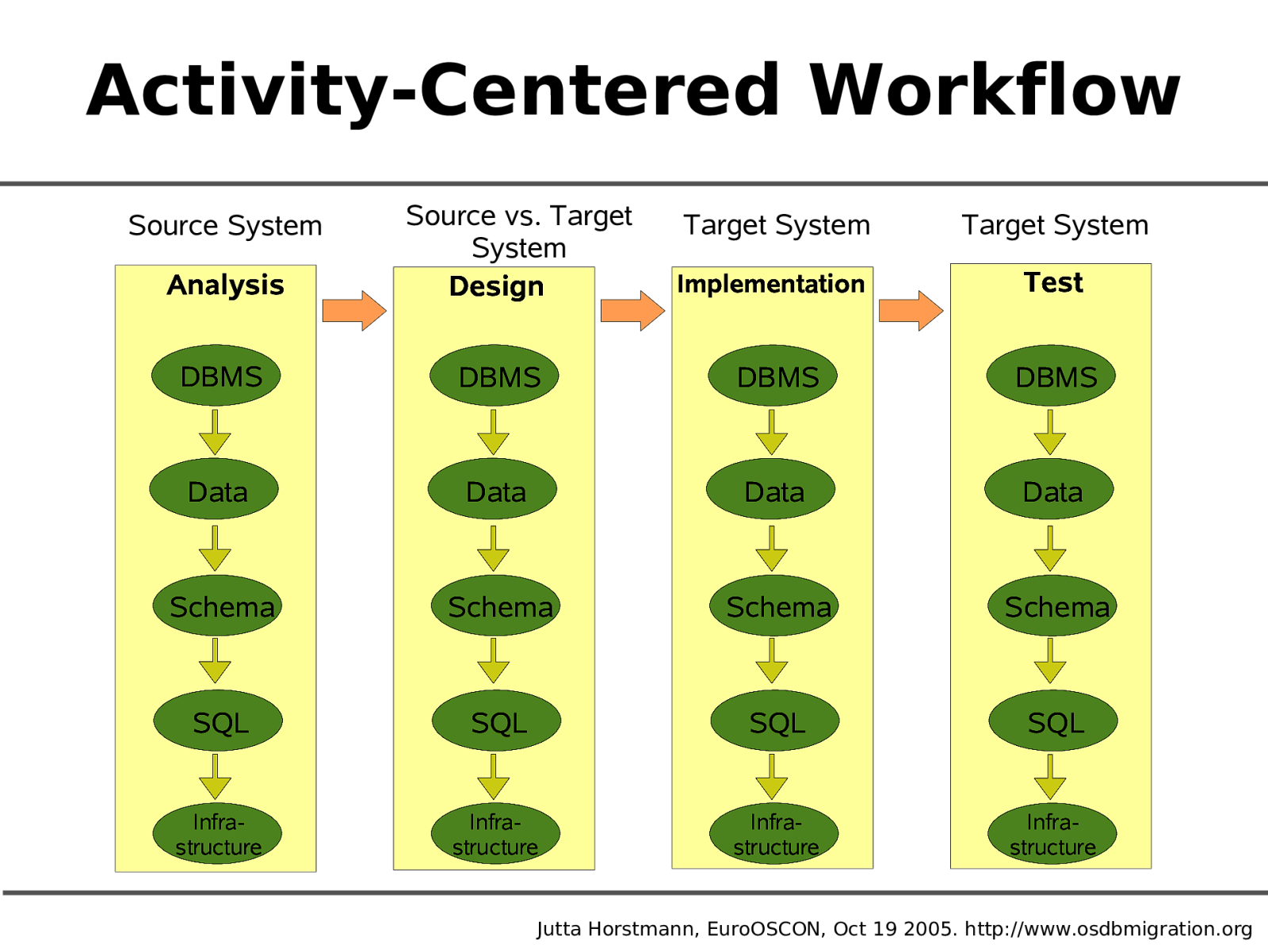
Activity-Centered Workflow Source System Analysis Source vs. Target System Design Target System Target System Implementation Test DBMS DBMS DBMS DBMS Data Data Data Data Schema Schema Schema Schema SQL SQL SQL SQL Infrastructure Infrastructure Infrastructure Infrastructure Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 14
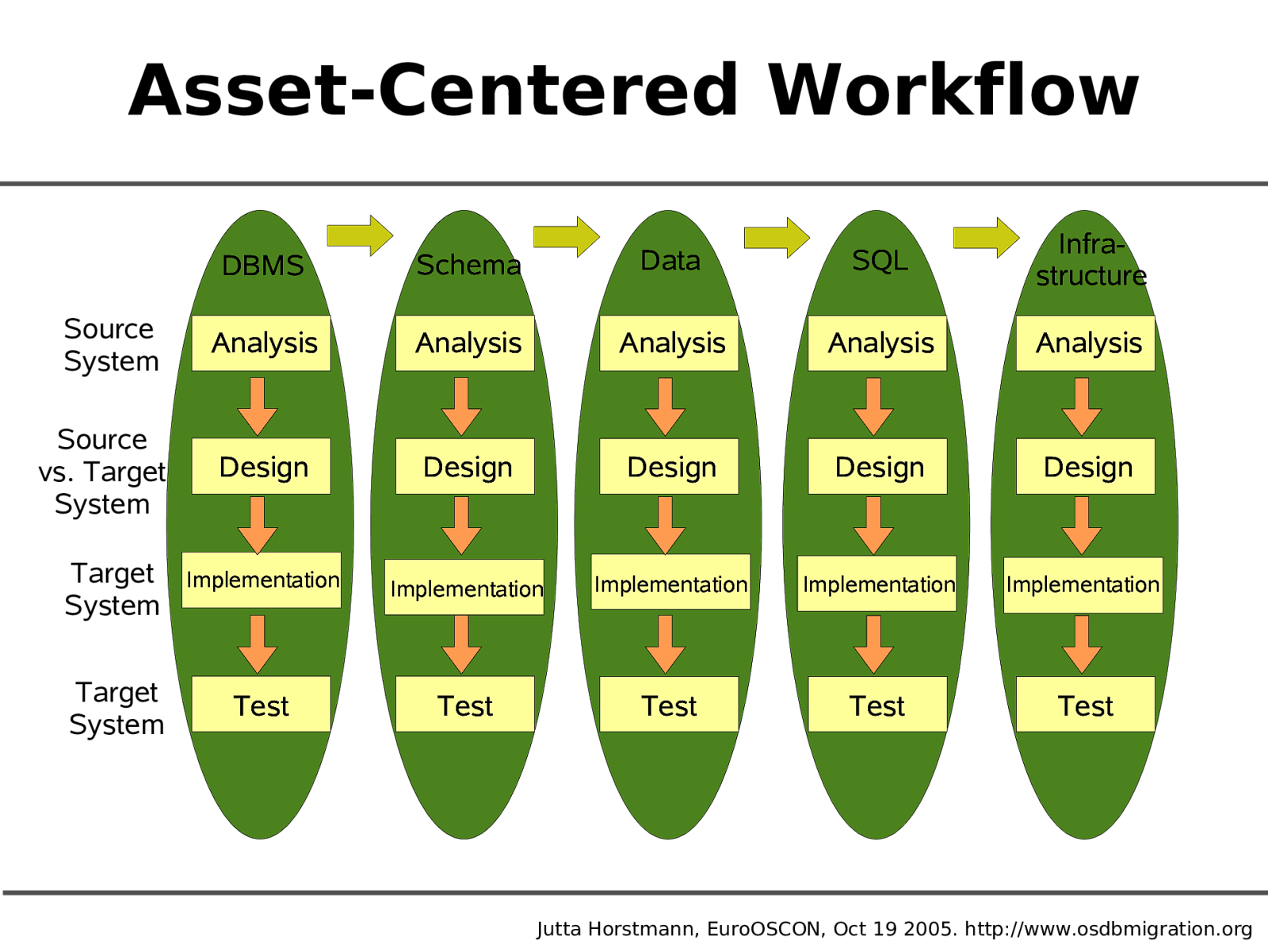
Asset-Centered Workflow DBMS Source System Source vs. Target System Analysis Analysis Design Desig n Data Schema Analysis Analysis Analysis Analysis Design Design Desig n Desig n SQL Analysis Analysis Design Desig n Infrastructure Analysis Analysis Design Desig n Target System Implementation Implementation Implementation Implementation Implementation Target System Test Test Test Test Test Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 15

Mixed-Model Workflow 1. Analyze the whole source system (all assets). 2. Migrate the DBMS software (design, implement, test). 3. Migrate the schema(s) (design, implement). 4. Migrate test data (design, implement, test). 5. Test the migrated schema(s) with the test data. 6. Migrate the client SQL (design, implement, test). 7. Migrate the database system’s infrastructure (d, i, t). 8. Cut-over: Full data migration. 9. Final testing and evaluation. Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 16

Analyze the whole system Analysis DBMS ● How is the software configured? Schema ● Complexity, quality of database design? Data ● How much data? Which condition? SQL ● SQL isolated? Standard compliant? Infrastructure ● Tools, Policies, Tuning …? Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 17
Where to look? Who to ask? Documentation Application History ? Data Flows Processes Data Dictionary Data Developers, Admins, Users Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 18

Migrate the DBMS software DBMS Design Implementation Test
- Choose Open Source DBMS 2. Devise mappings for configurations 3. Install & configure new software 4. Validate the working of the DBMS by using test databases and tools Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 19

Migrate the schema(s) 1. Provide abstraction (logical, conceptual?) Schema Design Implementation Test 2. Devise mappings to target system 3. Implement by loading converted schema into target system 4.Validate the schema’s correctness based on loading and querying test data. Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 20

Migrate Test Data 1. Correction and “cleansing” of “dirty data” Data Design Implement Test Data Test 2. Devise conversions and mappings 3. Transfer some test data: a) Extraction b)Transformation c) Load 4. Test: Errors at load? Query data! Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 21

Migrate Client SQL Database connectivity SQL ● Change ODBC/JDBC driver ● Switch client ● Client source available: Migrate! Design Implementation Test
- Provide abstraction (Standard SQL) OR 2. Convert directly to target SQL syntax 3. Test statements against schema and test data Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 22

Migrate Infrastructure ● Infrastructure Tools: Administration, Development, Design ● Change ODBC/JDBC driver ● Switch client Design Implementation Test ● Administrative Tasks – Gather policies and jobs – Implement them in the target system way Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 23

Full Data Migration (Cut-Over) 1. Strategy: a) Cold Turkey? Data Design Implementation Test b) Chicken Little? c) Butterfly? 2. Data Transfer: Extraction, Transformation, Load 3. Test: Errors at load? Query data! Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 24

“Cold Turkey” ● Take source system offline ● Extract data ● Transform data ● Load data into target system ● Take target system online Problems: ● How long offline? How much data? ● Fallback? Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 25
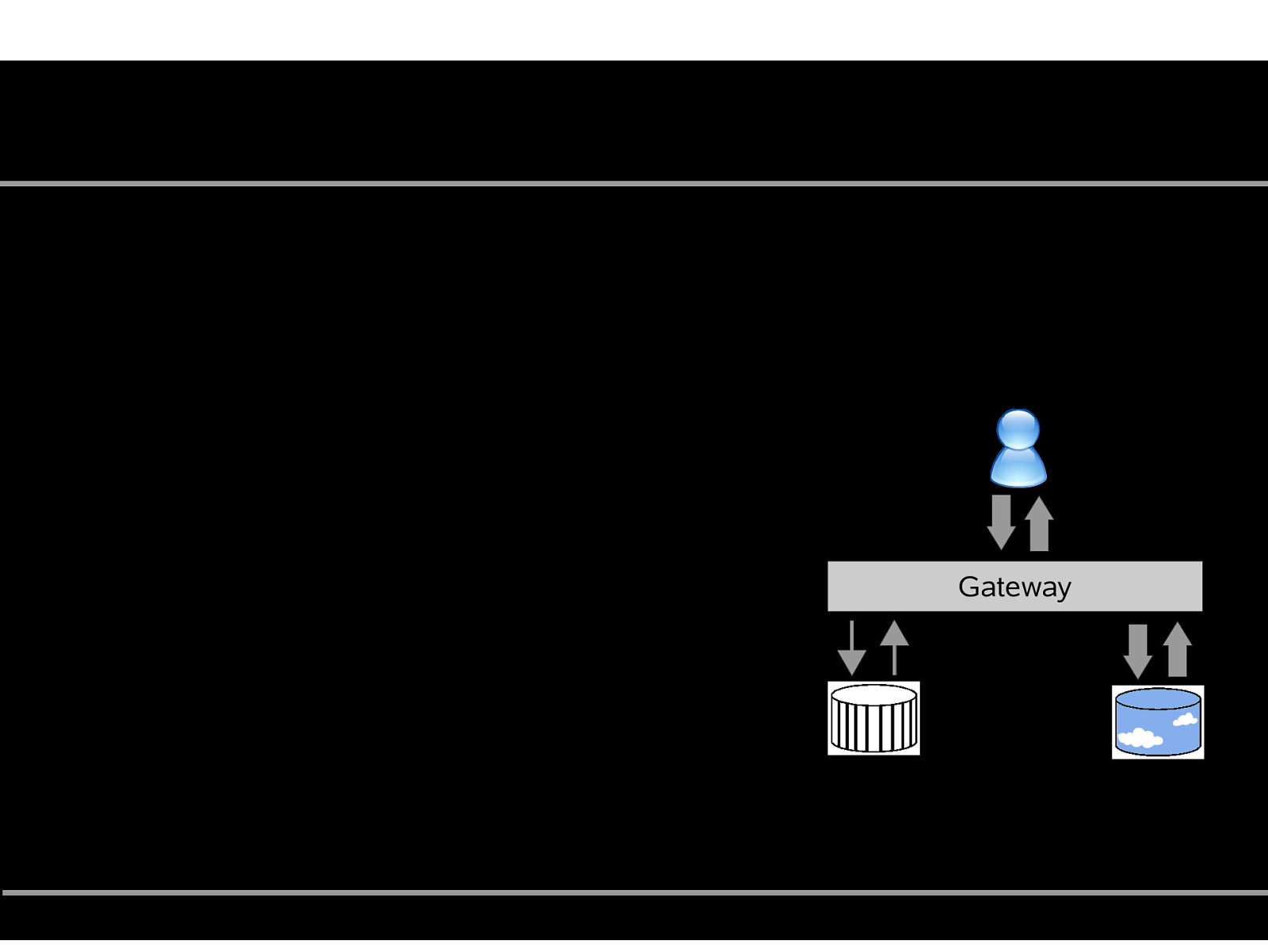
“Chicken Little” ● Source and target system operate in parallel ● “Gateway” coordinates and maps queries ● Incremental data migration Problem: Gateway ● Complex implementation ● Update consistency? Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 26

“Butterfly” ● Only source system online ● Data gets frozen read-only ● Store manipulation results in “Temp Store 0” ● Transfer frozen data ● Freeze TS0, store manipulation results in TS1 ● Transfer frozen data … and so on ● ● “Data Access Allocator coordinates and maps queries Problem: Complex implementation! Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 27
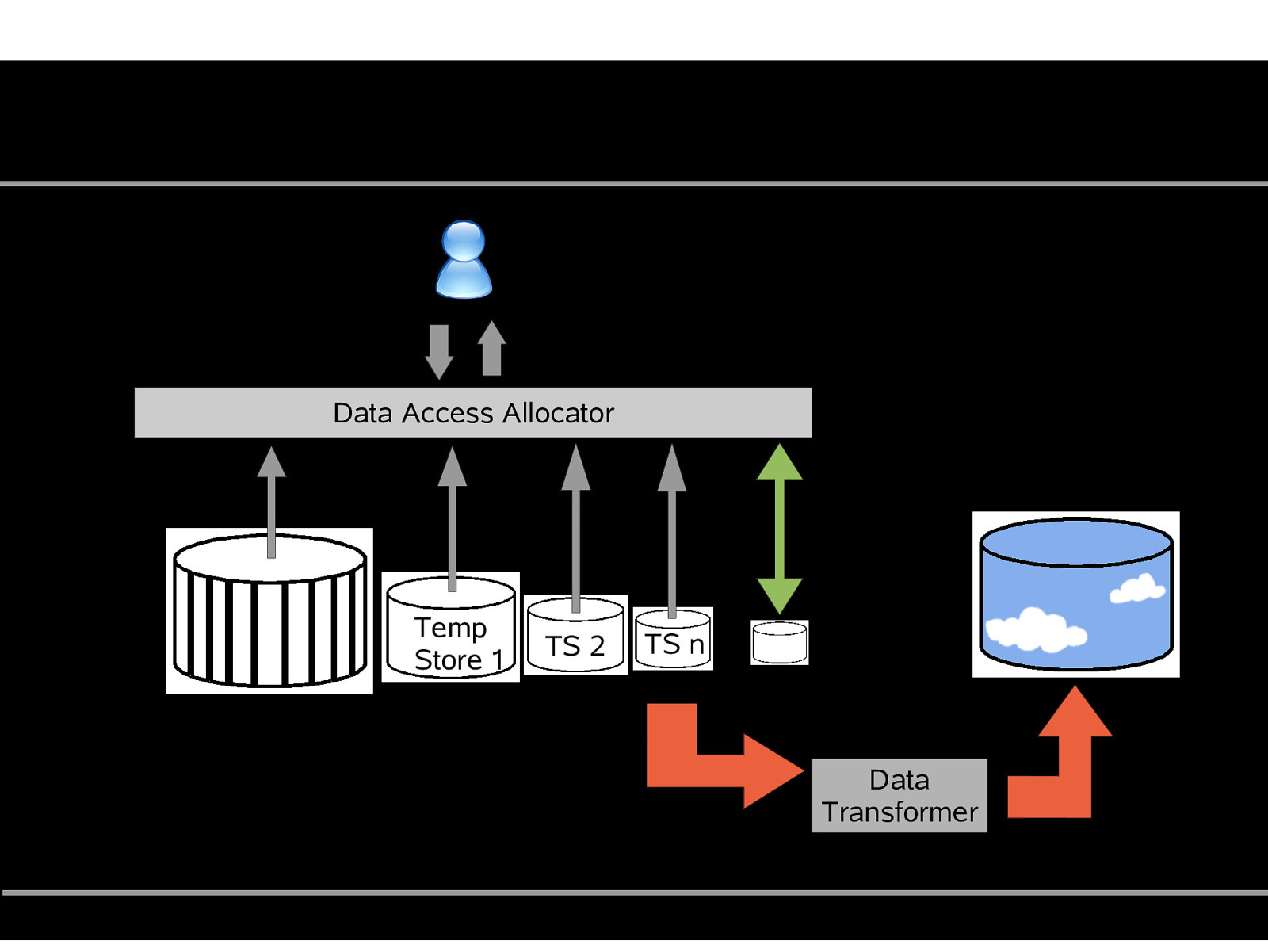
“Butterfly” Data Access Allocator Temp Store 1 Read-only TS 2 TS n TS n+1 Data Transformer Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 28

Summary: Problems ● Different SQL implementations ● User-defined data types/functions ● Stored Procedures ● Proprietary interfaces ● Flawed schema design ● Differences in Data Types ● “Dirty Data” ● Reserved Words Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 29

Help! - Migration Tools ● Automatization ● Integrity violation detection ● Re-Use ● Knowledge on source and target system ● Documentation ● Code Generation ● Script Scheduling ● Validation ● Speed! Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 30

Migration Tools, Examples ● Closed Source: – SQLWays (Ispirer). Only Windows. ● – ProgressionDB (Versora). Linux, Windows. ● ● Source: any, Target: MySQL, PostgreSQL MSSQL -> MySQL, PostgreSQL, Ingres Open Source: – Ingres Mio. $ Challenge (CA): shift2ingres – MySQL Migration Toolkit (MySQL AB) Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 31

Summary Migration to Open Source Databases ? ● Several Open Source options ● Migration is an ambitious project ● ● Workflow and results depending on state of source system Automatize the process, where possible! Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org
Slide 32

Questions? Jutta Horstmann, EuroOSCON, Oct 19 2005. http://www.osdbmigration.org